An Introduction: Water and Environmental Change in Sahel, Africa
Hello and Welcome to my blog!
My name is Kexin, and I am a third-year Earth Sciences student at UCL. I have been studying a module called "Water and Development in Africa" recently. I will be writing this blog exploring the relationship between water and environmental change in Africa, focusing on the Sahel region.
Why Water and Environmental Change in Africa?
Climate change is the biggest threat to humans in the 21st century, and "water is the primary medium through which we will feel the effects of climate change" (United Nations Water). And Africa is the most vulnerable region in the world to climate change (United Nations Climate Change, 2020). Half of its population lives in poverty, and 1 in 3 Africans suffers from water shortage (Mason et al.2019). Rising temperature and changing precipitation patterns that lead to more extreme climate events such as floods and droughts are hitting Africa harder than the rest of the world, threatening food and water security and economic development (WMO 2021).
Africa is also the fastest developing continent in the world. It has been experiencing very rapid land use and land cover changes such as urbanisation and deforestation. However, most of the changes are unplanned and disordered which further increased the water risk in Africa (Van den Berg et al., 2021).
Why the Sahel?
I decided to focus on the Sahel region of Africa because of its unique location. As shown in Figure 1, Sahel is a semi-arid transitional zone (around 12°N - 20°N) sandwiched between the arid Sahara Desert to the north and the humid Sudanian savanna to the south. It starches from the Atlantic coast on the west to the Red sea on the east through Mauritania, Senegal, The Gambia, Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, Nigeria, Chad, Sudan, Ethiopia, Eritrea and Djibouti (Heinrig,2011).
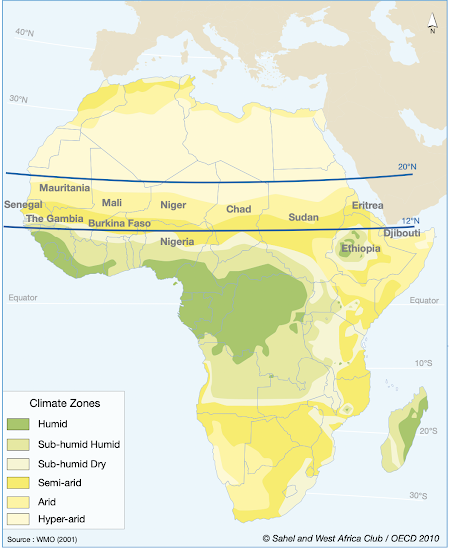 |
| Figure.1 The Sahel region, Africa (Heinrig, 2011) |
The following blogs will look into the relationship between environmental changes and rainfall variability in the Sahel, future projections, and some mitigation strategies adopted in the Sahel.
Hope you enjoy my blog. Thanks for reading!



Comments
Post a Comment